Discovery Overview
In 2024, a groundbreaking archaeological discovery was made in the dense jungles of Mexico’s Yucatán Peninsula. Using LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and drone-assisted imaging, researchers uncovered a subterranean Maya ceremonial complex within a cave system. The site, dating to the 7th–10th centuries CE, contained remarkably preserved artifacts, including intricately painted pottery, vivid murals depicting ritual scenes, and human skeletal remains arranged in ceremonial contexts. These findings shed light on Maya spiritual practices, particularly their beliefs in the underworld (Xibalba) and rituals associated with apocalyptic themes.
Significance of the Findings
- Underworld Beliefs: The murals and artifacts suggest the cave served as a sacred space for communicating with deities of the underworld. Skeletal remains, possibly sacrificial offerings, align with Maya narratives of cyclical destruction and renewal.
- End-of-World Rituals: Evidence of fire rituals and ceremonial deposits indicates practices tied to Maya calendrical cycles, such as the transition between cosmic eras.
- Cultural Complexity: The site challenges earlier assumptions that Maya ceremonial activities were confined to surface temples, revealing a layered spiritual geography.
Advanced Technologies in Archaeology
1. LiDAR: Revolutionizing Discovery
LiDAR technology has become indispensable in modern archaeology. By emitting laser pulses from aircraft, it penetrates dense vegetation to generate precise 3D maps of hidden structures. Key applications include:
- Mapping Subterranean Networks: In the Yucatán discovery, LiDAR identified cave entrances and subsurface chambers obscured by jungle canopy, enabling targeted excavations.
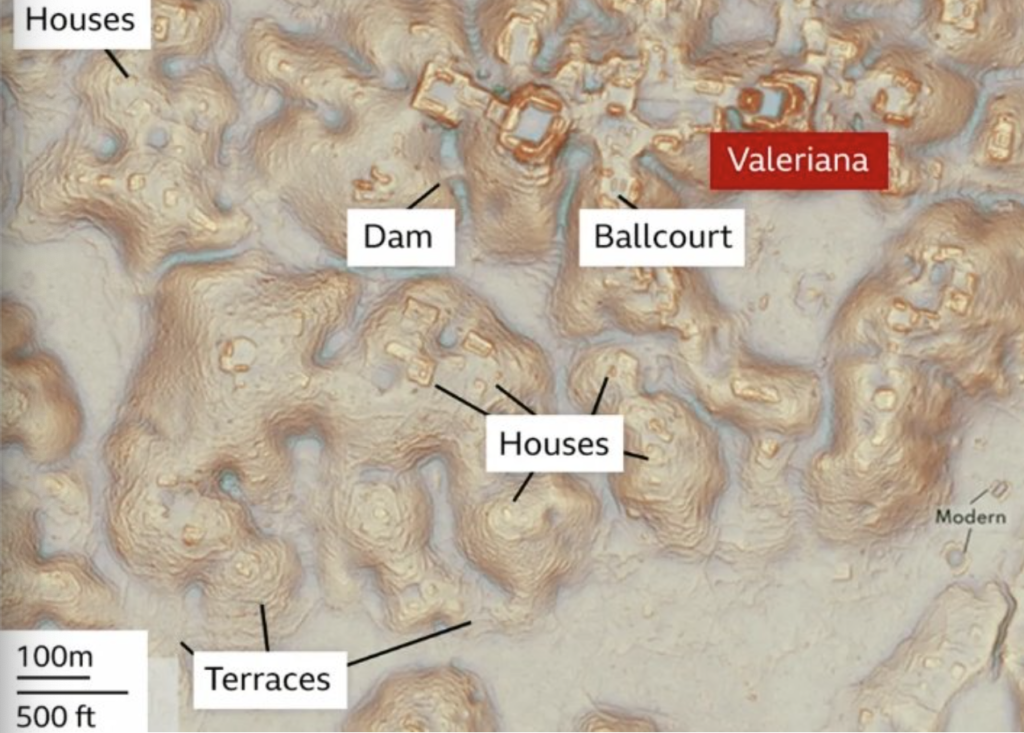
- Urban Planning Insights: Earlier LiDAR surveys in Mexico’s Campeche state revealed the lost city of Valeriana, a sprawling metropolis with pyramids, causeways, and ball courts, demonstrating the Maya’s sophisticated urban planning.
- Efficiency and Preservation: Unlike traditional excavation, LiDAR allows non-invasive exploration, preserving fragile sites while accelerating data collection.
2. AI-Driven Analysis
Artificial intelligence complements LiDAR by processing vast datasets and identifying patterns imperceptible to humans:
- Object Recognition: AI algorithms classify LiDAR data, distinguishing natural features from artificial structures (e.g., pyramids, causeways) with over 90% accuracy.
- Text and Image Decoding: In parallel discoveries, AI has decoded charred Roman scrolls from Herculaneum (damaged by Mount Vesuvius) and analyzed Maya glyphs, revealing previously inaccessible historical texts.
- Predictive Modeling: Machine learning models simulate ancient landscapes, such as Maya agricultural systems, to understand how environmental changes influenced societal collapse.
Case Study: Valeriana and Technological Synergy
The 2024 discovery of Valeriana, a Maya city in Campeche, exemplifies the synergy between LiDAR and AI:
- LiDAR Mapping: Over 6,600 structures, including pyramids and a circular theater, were mapped across 50 square miles. The city’s population (30,000–50,000) rivaled modern local towns.
- AI Analysis: Algorithms reconstructed settlement patterns, revealing a densely populated hub with interconnected causeways and ceremonial centers. This challenged the notion of tropical regions as “lands of civilizational collapse”.
Implications for Future Research
The integration of LiDAR and AI is transforming archaeology:
- Global Applications: From Cambodia’s Angkor Wat to Amazonian settlements, these technologies are uncovering lost cities and redefining historical narratives.
- Ethical Considerations: Balancing data accessibility with cultural preservation remains critical, especially for indigenous heritage sites.
For further details, refer to studies in Antiquity and Nature Archaeology.
Keywords: Maya civilization, LiDAR, AI in archaeology, Valeriana, underworld rituals.

